June 2015 virus activity review from Doctor Web
OREANDA-NEWS. July 02, 2015. June 2015 proved to be rather interesting in terms of information security. For instance, Doctor Web security researchers detected a number of hacker attacks on websites of different organizations, including the Russian Public Opinion Research Center (VCIOM). Moreover, during the first summer month, new malicious programs for Windows, OS X, and Android became widespread.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN JUNE
- Increased number of websites hacked by cybercriminals
- Growing number of installers of unwanted applications targeting OS X and distributed through the Internet
- New malicious programs for Windows and Android
Threat of the month
At the beginning of June 2015, Doctor Web analysts detected a new Trojan named Trojan.Proxy.27552 and designed to send out spam messages. This Trojan has a few peculiar characteristics; for example, it can cause BSOD (“Blue Screen of Death”) right after the beginning of the installation process. Another curious feature of Trojan.Proxy.27552 lies in the fact that it stores the list of command and control servers' addresses in the Windows system registry.
The main purpose of Trojan.Proxy.27552 is to send spam messages together with a remote spam server. Curiously enough, links from the messages sent by the Trojan direct users to hacked websites. Detailed information regarding this malware can be found in the review published by Doctor Web.
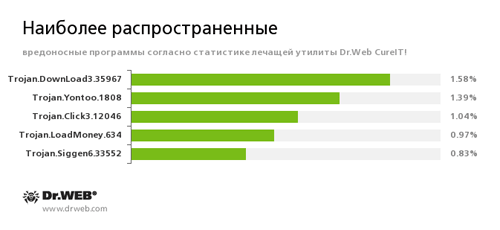
According to the statistics gathered by Dr.Web CureIt!
Trojan.DownLoad3.35967
A Trojan that can download other malicious programs from the Internet and install them on the infected computer.
Trojan.Yontoo
Browser plug-ins that display advertisements on webpages.
Trojan.Click
Malicious programs designed to generate traffic for various websites by redirecting users to the corresponding webpages.
Trojan.LoadMoney
A family of downloader Trojans generated by servers belonging to the LoadMoney affiliate program. These applications download and install various unwanted programs on the infected system.
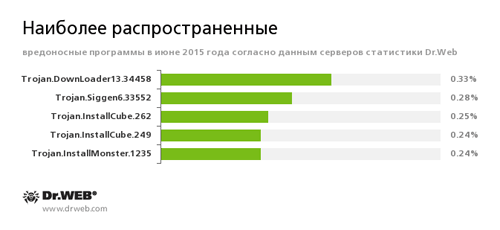
According to Doctor Web statistics servers
Trojan.DownLoader13.34458
A Trojan that can download other malicious programs from the Internet and install them on the infected computer.
Trojan.InstallCube
A family of downloader programs designed to install unwanted and useless applications on the user’s computer.
Trojan.Installmonster
A family of malicious programs created using the Installmonster affiliate program. These applications download and install various unwanted programs on infected computers.
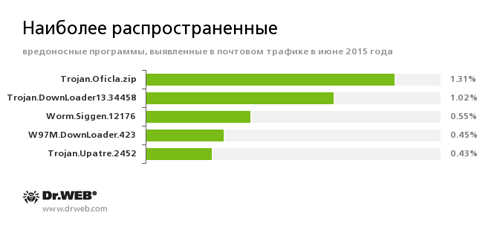
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
Trojan.Oficla
A family of Trojans mainly distributed via email messages. Once one of these Trojans infects a system, it hides its further activity. Trojan.Oficla connects the computer to a botnet, which allows cybercriminals to upload other malicious software to the compromised machine. After the system gets infected, cybercriminals that control the botnet get control over the victim’s computer. In particular, they become able to upload, install, and use any malicious software they choose.
Trojan.DownLoader13.34458
A Trojan that can download other malicious programs from the Internet and install them on the infected computer.
W97M.DownLoader.423
A malicious program mainly distributed via email messages with attached Microsoft Word documents. It is designed to download other malware to the compromised computer.
Trojan.Upatre
A family of Trojans that covertly download and install other malicious applications on the infected computer.
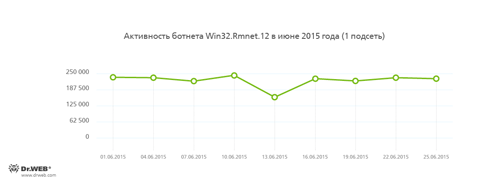
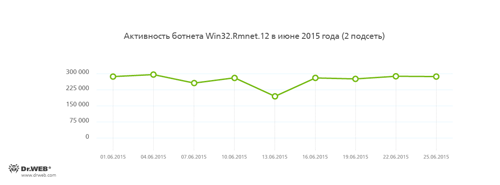
Botnets
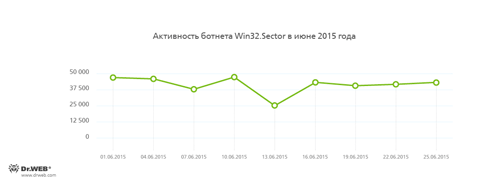
Doctor Web security researchers continue to monitor a number of active botnets. Among them is a botnet created by cybercriminals using the file infector Win32.Rmnet.12. The average daily activity of the botnet's two subnets is shown in the following graphs:
Rmnet is a family of viruses spread without any user intervention. They can embed content into loaded webpages (this theoretically allows cybercriminals to get access to the victim's bank account information) as well as steal cookies and passwords stored by popular FTP clients and execute other commands issued by cybercriminals.
The botnet consisting of computers infected with the Win32.Sector file virus is still active. This malicious program can perform the following actions:
- Download various executable files via a P2P network and launch them on infected machines.
- Inject its code into running processes.
- Prevent some anti-viruses from operating and block access to the websites of their respective developers.
- Infect files on local disks, removable media (where the malware creates the autorun.inf file during the infection process), and in shared folders.
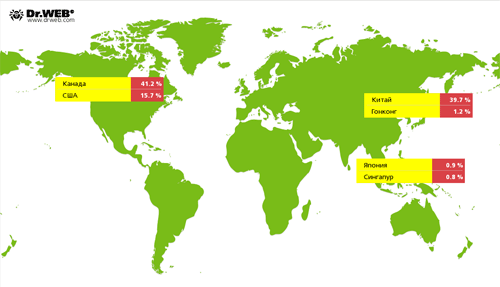
In June, attacks on Internet resources with the use of Linux.BackDoor.Gates.5 became considerably less frequent. In comparison with the previous month, the number of attacked IP addresses decreased by 76.6 per cent and was estimated 1,284. Cybercriminals also changed the focus of their attacks. Thus, Canada became the country leading in the number of compromised resources, while China and the United States were ranked second and third respectively.
Encryption ransomware
The number of requests for decryption received by the Doctor Web technical support service
| May 2015 | June 2015 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| 1,200 | 1,417 | + 18% |
The most common ransomware programs in June 2015
- Trojan.Encoder.858
- Trojan.Encoder.567
- BAT.Encoder
Dr.Web Security Space 10.0 for Windows
protects against encryption ransomware
This feature is not available in Dr.Web Anti-virus for Windows
| Preventive protection | Data Loss Prevention |
|---|---|
 |  |
OS X
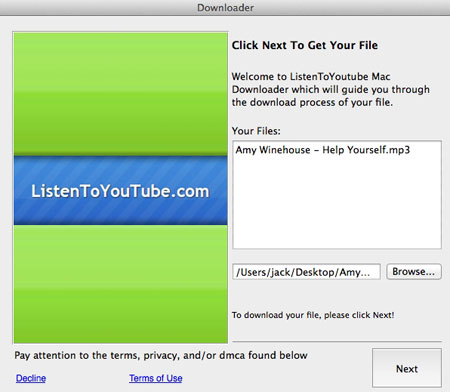
Adware and installers of unwanted applications are found among the most frequently distributed malicious programs that target OS X. In June, a suchlike malware was added to virus databases under the name of Adware.Mac.MacInst.1.
Once Adware.Mac.MacInst.1 is run, it demonstrates a dialog with the information on the file the user wanted to download.
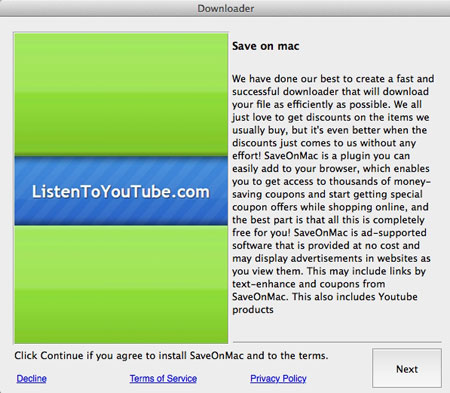
After the “Next” button is clicked, the malware displays a partnership agreement informing the user that in addition to the file itself some other components will be installed.
Among these components, there is a program detected by Dr.Web as Trojan.VIndinstaller.3. This application, in turn, installs malicious plug-ins for Safari, Firefox, and Chrome that are detected as Trojans belonging to the Trojan.Crossrider family. Find out more about the malware in this news article.
Dangerous websites
In June 2015, a number of webpages on the official website of the Russian Public Opinion Research Center (VCIOM) were temporarily added to Dr.Web virus databases as Internet resources distributing malicious software. This is due to the fact that both Russian (wciom.ru) and English (wciom.com) versions of VCIOM's website were hacked by cybercriminals. On the compromised server, hackers created a special section where they planted a number of webpages with most frequently searched titles. These pages contained a link to download a file detected by Dr.Web as a malware belonging to the Trojan.DownLoader family. Using this downloader, cybercriminals were able to install a mining application and other malicious programs on affected computers. Judging by the statistics, tens of thousands of users fell victim to this fraudulent scheme.
During June 2015, 978,982 URLs of non-recommended sites were added to Dr.Web database.
| May 2015 | June 2015 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 221,346 | + 978,982 | + 342.28 % |
Malicious and unwanted programs for Android
In June, cybercriminals continued to target users of Android devices. Moreover, a number of various unwanted and malicious applications for the mentioned operating system were detected by Doctor Web security researchers. Among the most noticeable events related to malware for Android we can mention
- Attacks carried out using various banking Trojans and aimed at stealing money from bank accounts of Android devices' owners
- Emergence of new Android ransomware
- New cases of downloader Trojans being employed by cybercriminals to distribute malicious software
- Growing number of SMS Trojans




Комментарии